Ever tried stopping a bout of hiccups? If you have, you would know that hiccups go away when they jolly well wish to, not when you order them to. A hiccup (or a singultus, to call it by its proper medical name) is an involuntarily or reflex action happening inside your body. You cannot control,
Ever tried stopping a bout of hiccups? If you have, you would know that hiccups go away when they jolly well wish to, not when you order them to. A hiccup (or a singultus, to call it by its proper medical name) is an involuntarily or reflex action happening inside your body. You cannot control, check or stop it.
Hiccups may be a nuisance but the good thing is that these rarely last for long. A few seconds or minutes of going hic-hic and hiccups can disappear as suddenly as they cropped up. It is a good thing because if hiccups lasted longer you would have trouble breathing, eating or talking or doing anything that requires focus. Imagine hiccupping while humming a song or talking to friends or hitting a ball or eating your favourite dishes!
So let’s get to know the factors that cause hiccups.
What causes hiccups
If everything does happen for a reason, scientists and doctors of the world haven’t yet figured out precisely why nature has given us hiccups in the first place but we do know the causes of hiccups.
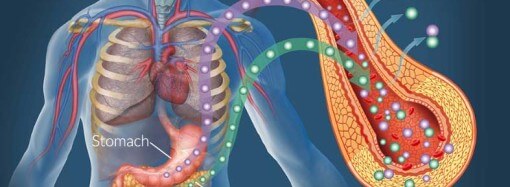
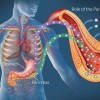
The three internal body parts involved in the process of hiccups are the diaphragm, the phrenic nerve and the epiglottis. Diaphragm is a large sheet of muscle that holds your chest organs away from the organs in the abdomen. The phrenic nerve is the controller of diaphragm. Epiglottis is a fleshy lid inside the throat that flaps shut the voice box area at eating time to ensure that foods and drinks go to your food pipe and not your wind pipe.
When we breathe in, the diaphragm moves down. When we breathe out, it moves up. If the nerve controlling the diaphragm, the phrenic nerve is irritated for some reason, the diaphragm gets spasms. A spasm in turn causes a short and quick breath which in turn activates epiglottis to suddenly close shut the opening of the windpipe by falling like a trapdoor over an opening. This sudden fall of epiglottis creates the unmistakable ‘hic-hic’ sound associated with hiccups. When this entire chain of events occurs one after another, a hiccup is born.
What causes hiccups in adults
An overfull stomach is the most common cause of hiccups. Overeating, gulping down food too fast, eating over spicy food, drinking too much alcohol, smoking, drinking hot drinks immediately after chilled ones or vice versa, all of these can cause hiccups in adults. Too much stress or excitement can also trigger hiccups.
What causes hiccups in babies
Babies hiccup more than adults do. Actually even unborn babies hiccup while still in the womb. Small babies can get hiccups if they are overfed or if they swallow too much air. This distends their tiny tummies which then irritates the diaphragm leading to hiccups. Babies’ hiccups usually go away if given smaller feeds, burped regularly and holding the baby upright for shot durations.
How to stop hiccups
You rarely need a doctor to treat hiccups. There are hundreds of home remedies all over the world for stopping hiccups in adults. Basically speaking, all these home remedies work on the principle of tricking body and mind into believing that they have more pressing concerns to handle than making hiccups. Drinking chilled water, holding your breath, breathing into a paper bag, thrusting fingers into ears, getting scared, yanking your tongue, tickling the roof of your mouth, eating a spoonful of peanut butter slowly, slowly chewing an antacid tablet and many more besides these. Experience shows that many of these do work but their effectiveness is not easy to verify as most hiccups disappear on their own and you never really know for sure if it was the remedy that did the trick or it just happened naturally.
Occasional hiccups are quite harmless, long lasting ones are not. If a hiccup spell lasts longer than a few hours, you need to visit the doctor to rule out any potentially serious underlying health problems.
So have you ever had a long or short hiccup episode? Did it go away on its own or did you do something to make it go away? Do share your hiccup experience with us.












































Leave a Reply